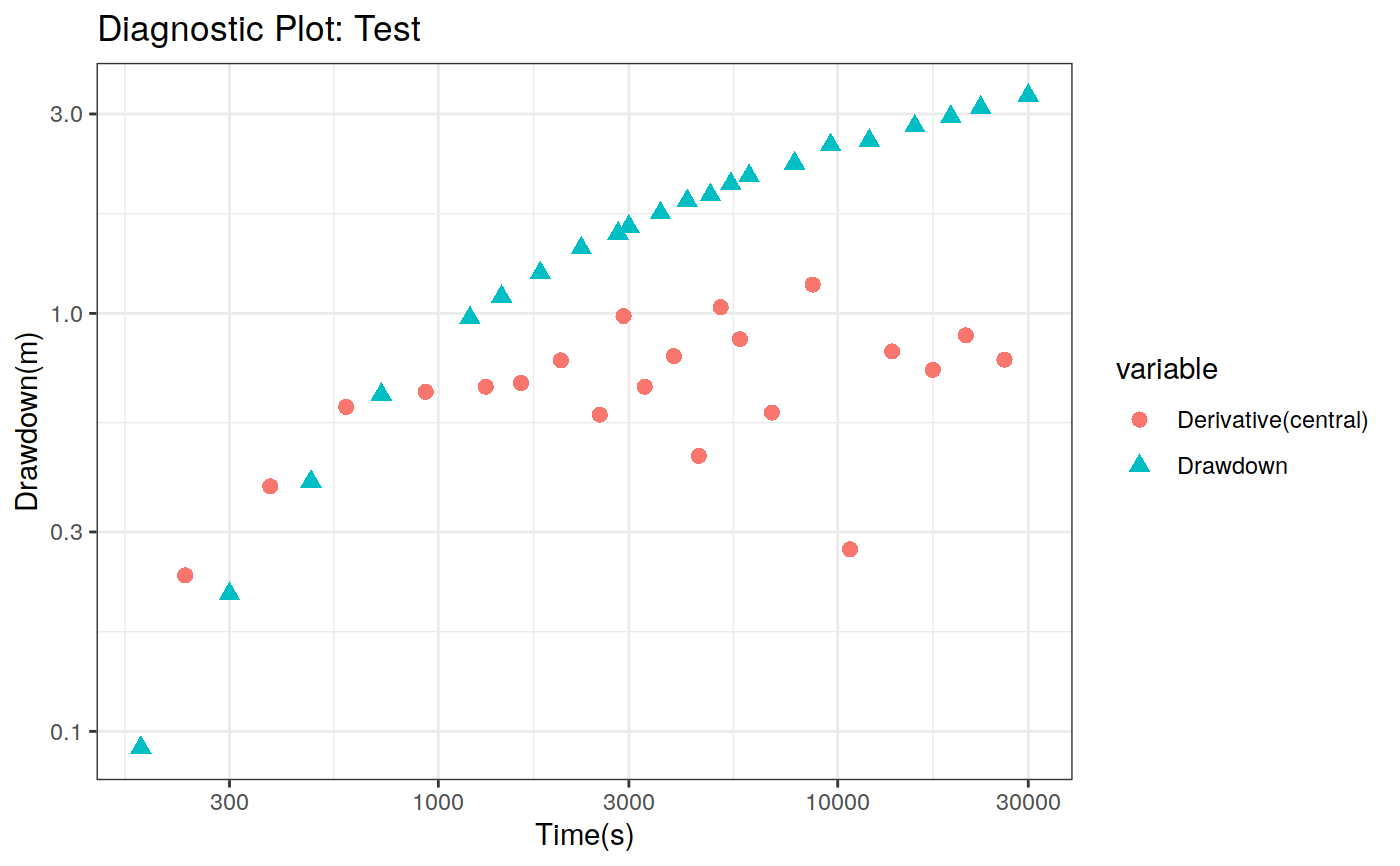
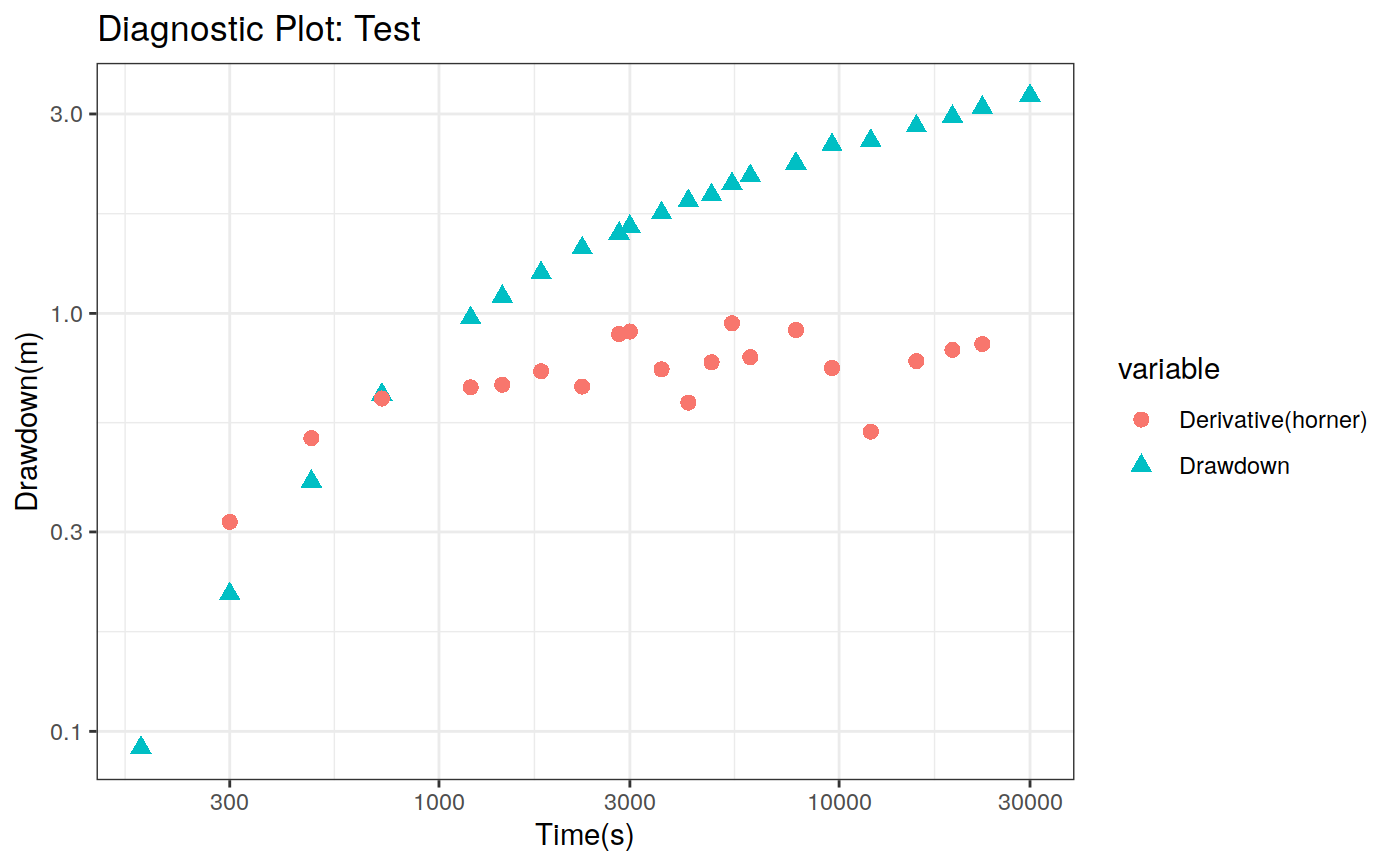
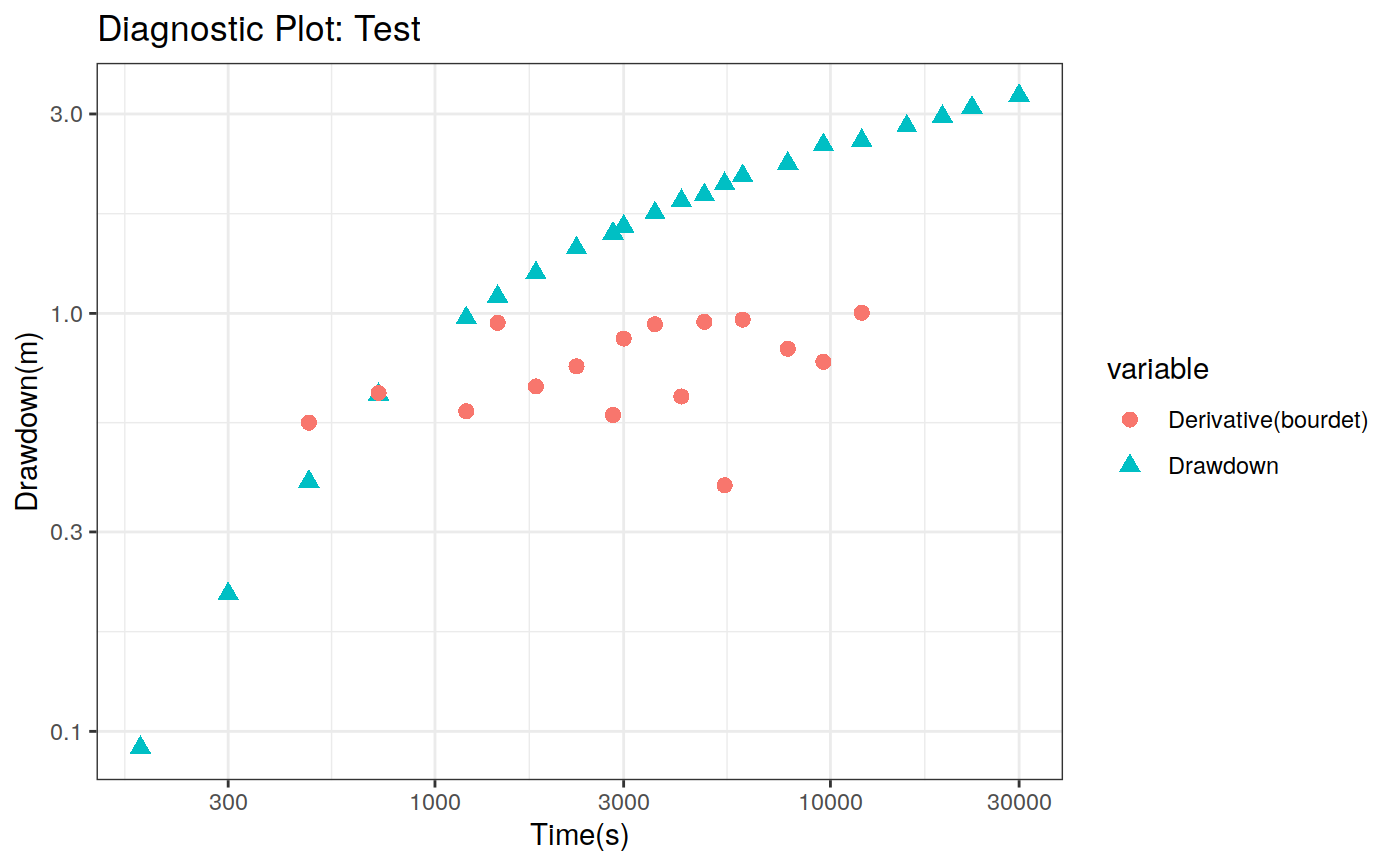
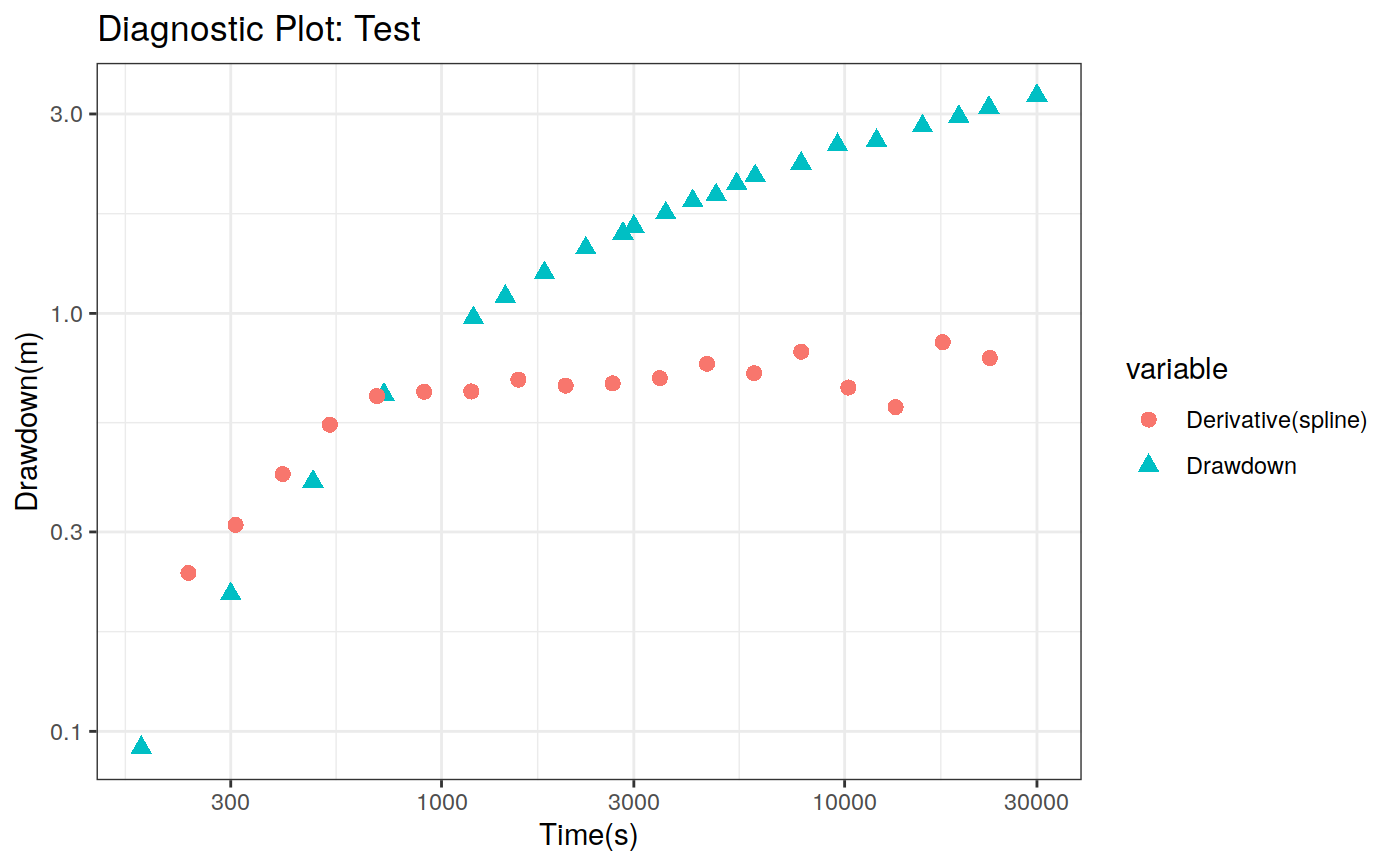
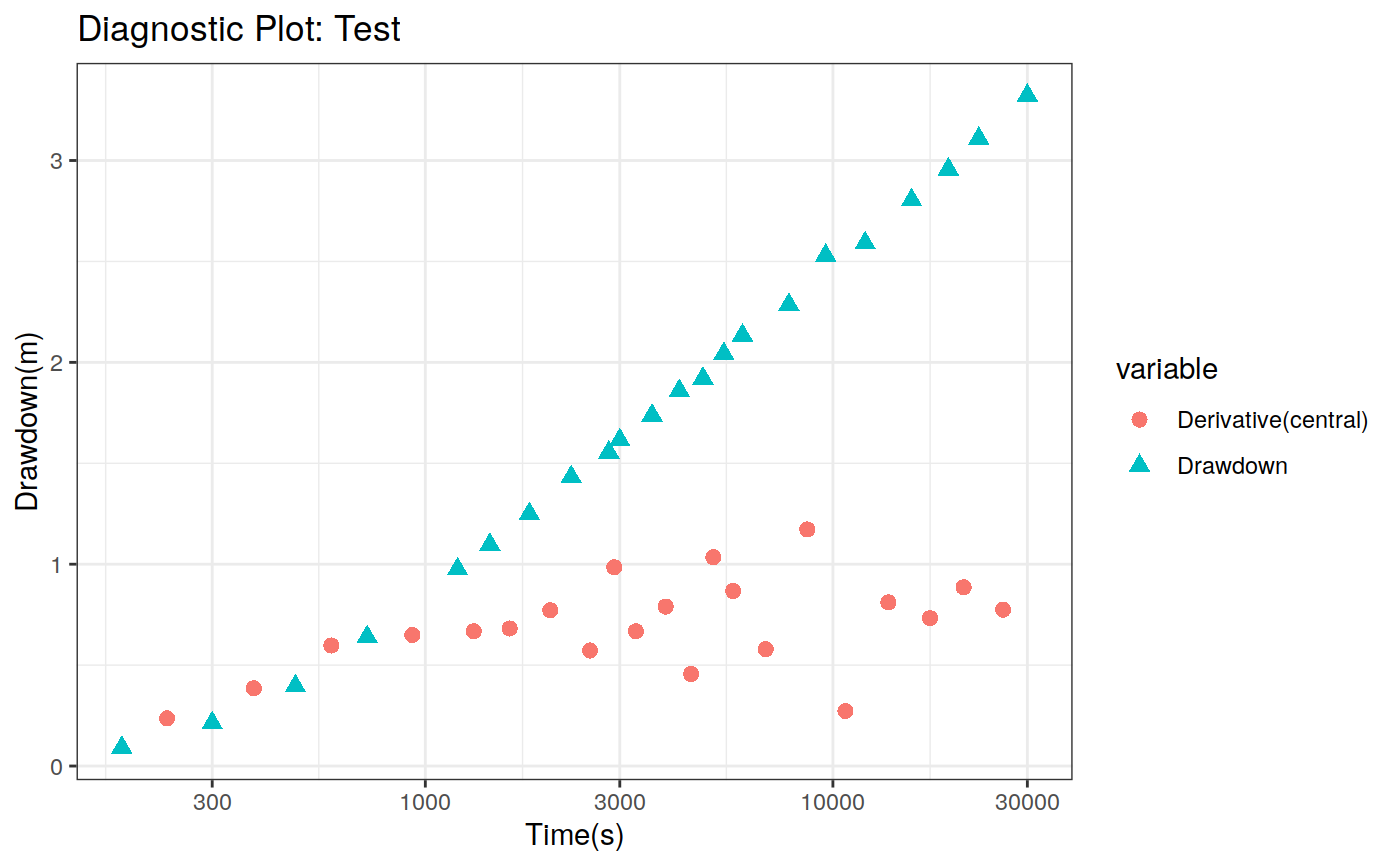
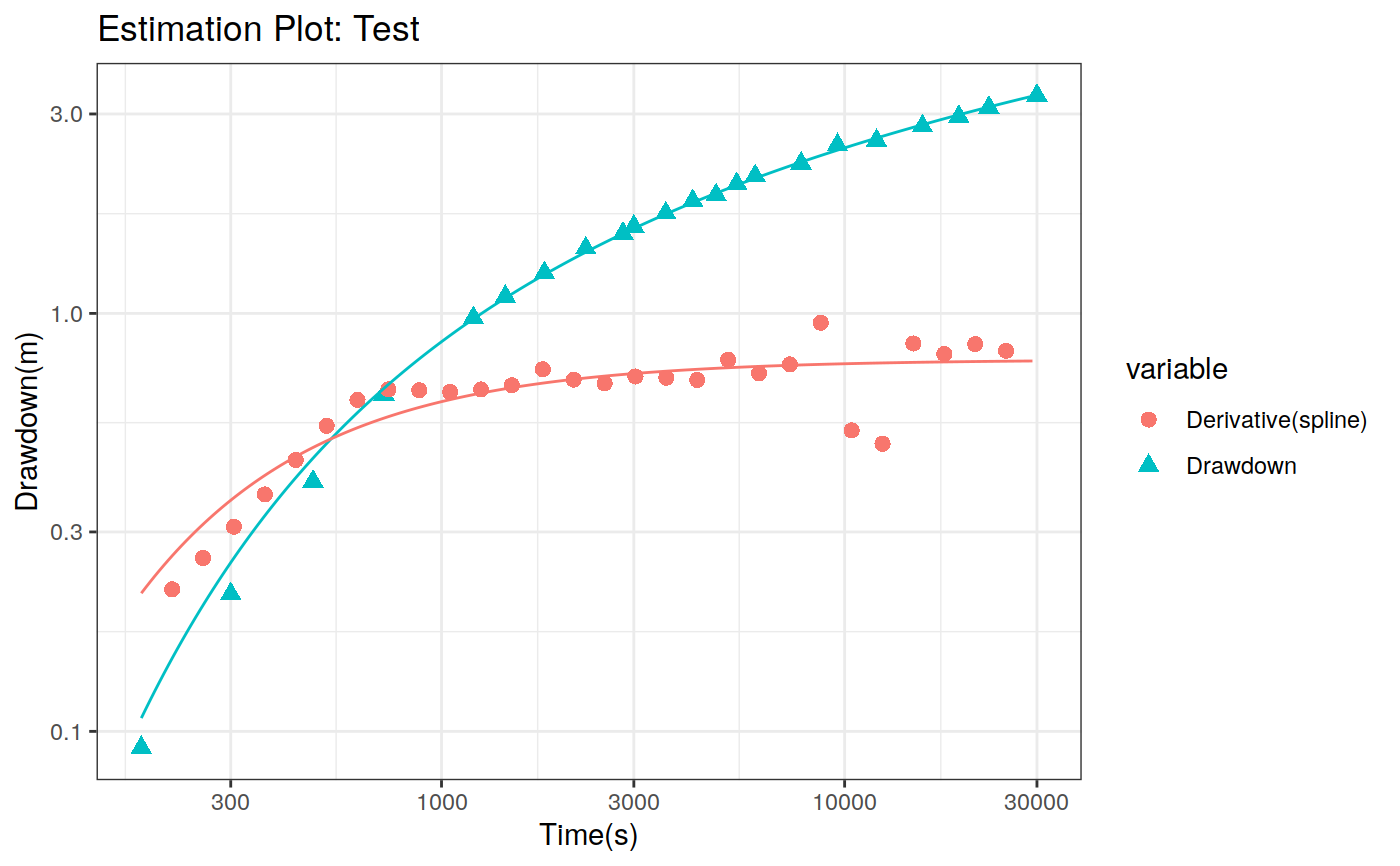
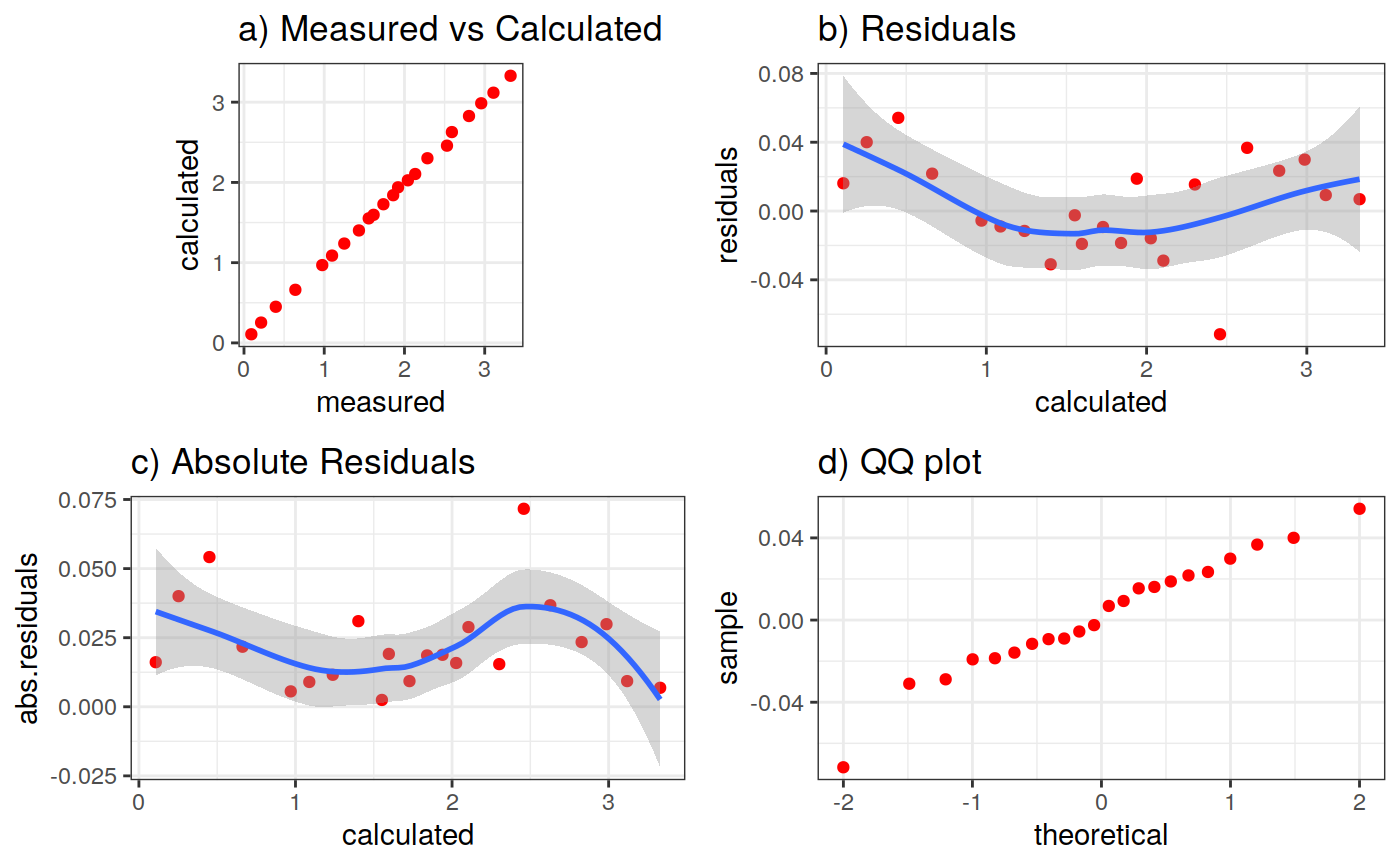
Function to plot the pumping test data. This function can create two different types of plots: diagnostic and estimation. The diagnostic plot includes the drawdown vs time plot and the derivative of drawdown with respect to the log of time. This derivative can help in the identification of the flow regime that occurred when the data was acquired.
# S3 method for pumping_test plot(x, type = c("diagnostic", "estimation", "model.diagnostic", "uncert", "mcmc.trace", "mcmc.run_mean", "mcmc.compare", "mcmc.autocorr", "sample.influence"), dmethod = "central", d = 2, scale = "loglog", y.intersp = 0.5, slug = FALSE, legend = TRUE, results = FALSE, cex = 1, ...)
Arguments
| x | A pumping_test object |
|---|---|
| type | Type of plot. Current options include
|
| dmethod | Method to calculate the derivative (central, horner, bourdet, spline) |
| d | Derivative parameter. If method is bourdet then d is a parameter to specify the number of lags in the derivative. If method is spline then d is the number of points used to calculate the derivative. |
| scale | Option to define a loglog or semilog diagnostic plot |
| y.intersp | Numeric value to define the interspacing between lines in the legend |
| slug | Logical flag to indicate a slug test |
| legend | Logical flag to indicate if legend is included (only for estimation plot) |
| results | Logical flag to indicate if the estimation results are going to be included in the estimation plot |
| cex | character expansion factor relative to current par("cex"). This is a parameter of the plot functions. |
| ... | Additional parameters for the plot, points and lines functions. |
See also
Other base functions: additional.parameters<-,
confint.pumping_test,
confint_bootstrap,
confint_jackniffe,
confint_wald, estimated<-,
evaluate, fit.optimization,
fit.parameters<-,
fit.sampling, fit,
hydraulic.parameter.names<-,
hydraulic.parameters<-,
model.parameters, model<-,
plot_model_diagnostic,
plot_sample_influence,
plot_uncert,
print.pumping_test,
pumping_test, simulate,
summary.pumping_test
Examples
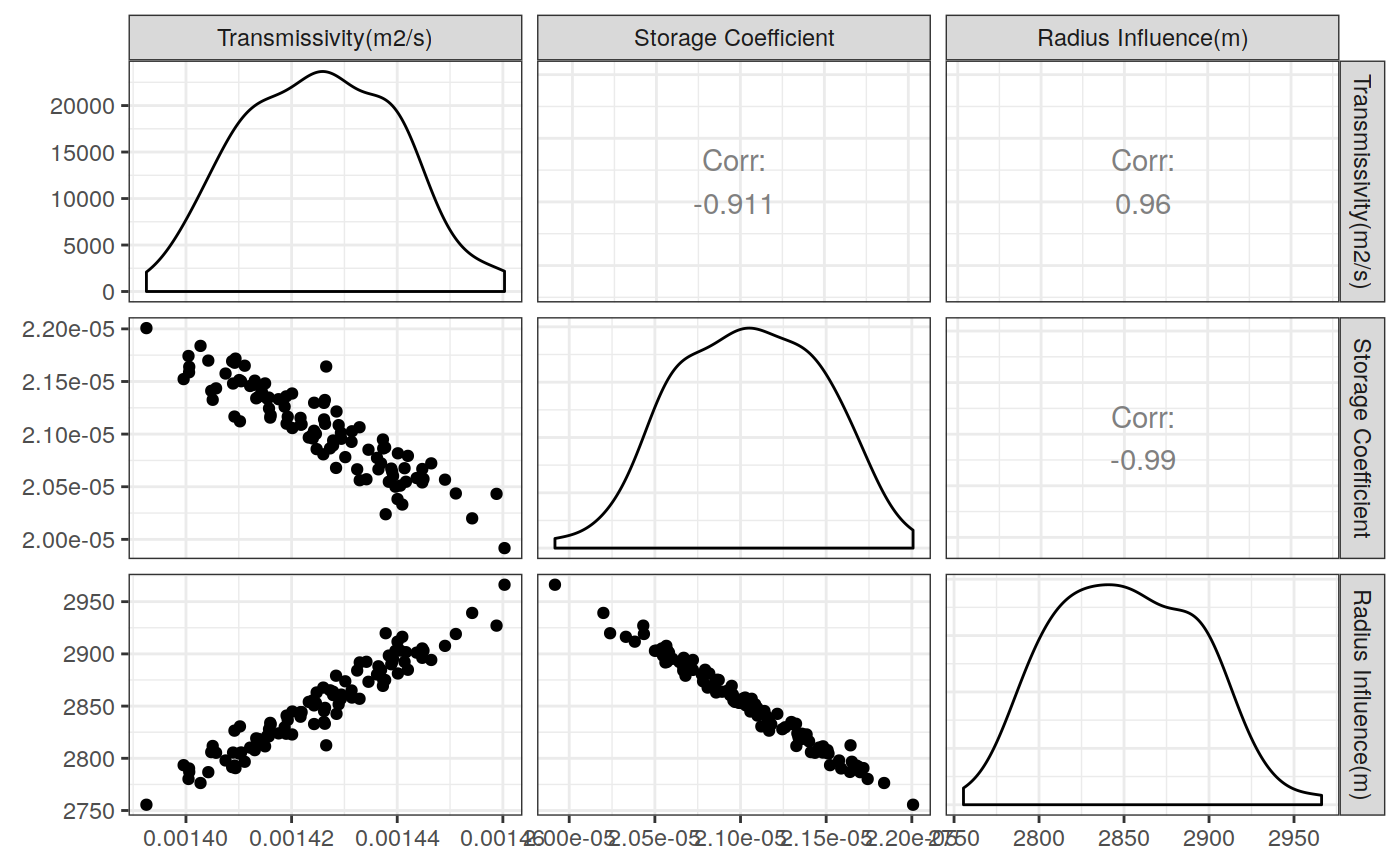
# Define a pumping test data(theis) ptest <- pumping_test("Test", Q = 1.388e-2, r = 250, t = theis$t, s = theis$s) # Diagnostic plot using default parameters plot(ptest)#>#>#>#>#>#estimation Plot ptest.fit <- fit(ptest, "theis") hydraulic.parameters(ptest) <- ptest.fit$hydraulic_parameters fit.parameters(ptest) <- ptest.fit$parameters model(ptest) <- "theis" estimated(ptest) <- TRUE plot(ptest, type = 'estimation', dmethod = "spline", d = 30, results = FALSE)#>#>#>#>#> TableGrob (2 x 2) "arrange": 4 grobs #> z cells name grob #> 1 1 (1-1,1-1) arrange gtable[layout] #> 2 2 (1-1,2-2) arrange gtable[layout] #> 3 3 (2-2,1-1) arrange gtable[layout] #> 4 4 (2-2,2-2) arrange gtable[layout]# Uncertainty plot (bootstrap) ptest.confint <- confint(ptest, level = c(0.025, 0.975), method = 'bootstrap', n = 30, neval = 100) hydraulic.parameters(ptest) <- ptest.confint$hydraulic.parameters hydraulic.parameter.names(ptest) <- ptest.confint$hydraulic.parameters.names plot(ptest, type = 'uncertainty')#>